
The human body is a complex machine, with various parts working in tandem to keep us alive and healthy. This concept lies at the heart of holistic medicine. But one of the most intriguing connections many of us don’t consider is the tongue-brain connection. This connection is so powerful that it is used in medical treatments for pain relief, depression, and more! Read on to learn more about the tongue-brain connection and how you can use it to promote pain relief.
The Tongue: More Than Just a Tasting Tool
Most of us think of the tongue as the organ that allows us to taste and savor the flavors of our favorite foods. However, the tongue is so much more than that. It is also a powerful sensory organ that provides vital information to the brain about the texture, temperature, and other properties of the food we eat.
Your tongue is covered in tiny bumps called papillae containing taste buds. These taste buds detect different flavors and send signals to the brain to interpret the taste. However, the tongue also contains nerve fibers responsible for transmitting other sensory information, such as the temperature and texture of the food. This information is essential for our brain to determine whether the food is safe to eat or not.
The Command Center of the Body
The tongue is connected to the brain through a network of nerves and neurons that allow for the transmission of sensory information. When the tongue detects a taste or texture, it sends a signal to the brain, which interprets the data and sends signals back to the tongue to respond accordingly.
The Fascinating Science Behind the Tongue-Brain Connection
Recently, scientists have discovered that the tongue and brain work together in previously unknown ways. For example, recent studies have shown that the tongue and brain can work together to influence each other’s functions.
One study found that the taste of sweetness can increase brain activity in regions associated with reward and motivation, suggesting that the tongue-brain connection plays a crucial role in our food choices and preferences.
Another study found that our emotions influence the way we perceive flavors. The study found that people in a negative emotional state rated sweet and sour flavors less pleasant than those in a positive emotional state. This suggests that the tongue-brain connection is influenced by our emotions and can impact how we experience flavors.
The tongue-brain connection also plays a critical role in developing speech and language. The tongue produces sounds and movements that form the basis of speech. The brain processes these sounds and movements, allowing us to understand and create language.
According to Dr. Norman Doidge, author of the bestselling book “The Brain That Changes Itself,” the disruption and subsequent imbalance of electrical activity within the brain is a significant cause of neurological symptoms.
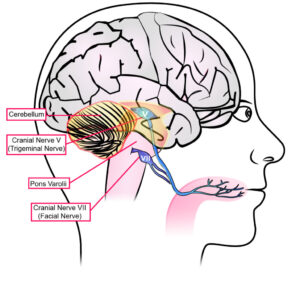
Dr. Doidge found that electrical stimulus to the brainstem, specifically the cranial nerves that carry information between the brain and the body, can help bring the electrical activity in brain cells back into balance.
The pons, a critical part of the brain, contains many crucial cranial nerve synapses that help to relay impulses governing body regulation, facial motor control, balance, pain, and other functions. Revived cells can often reintegrate into the brain’s neural networks, enabling neuroplastic healing.
Learn more about the pons in our blog here!
How Tongue Stimulation Can Reduce Pain

One of the most promising uses of the tongue-brain connection is pain relief. In our experience, stimulating the tongue with microcurrent can significantly reduce pain in various body parts.
Microcurrent stimulation involves using a low-level electrical current to stimulate nerves in the tongue. This stimulation sends signals to the brain, which releases natural pain-relieving chemicals such as endorphins and enkephalins.
Studies have shown that microcurrent stimulation of the tongue can significantly reduce pain in various conditions, including:
- Chronic back pain
- Fibromyalgia
- Migraines
- Neuropathic pain
The benefits of using microcurrent stimulation for pain relief include the following:
- Non-invasive treatment
- No known side effects
- Quick results
But there are more things it can do! In this short video, Dr. Rob talks about the many illnesses or chronic pain issues that can be treated with tongue stimulation.
The Role of PONs in the Tongue-Brain Connection
The tongue-brain connection works through the trigeminal nerve, one of the head’s largest nerves. The trigeminal nerve has three branches, each responsible for different facial and mouth sensations.
Recent research has shown that the anterior branch of the trigeminal nerve, also known as the PONs (pterygoid branch of the trigeminal nerve), plays a crucial role in the tongue-brain connection. The PONs transmit sensory signals from the tongue to the brain.
Studies have shown that stimulating the PONs with microcurrent can enhance the tongue-brain connection and improve pain relief. This is because the PONs are directly connected to the brainstem, which is responsible for regulating pain perception.
The Flexible Y Tool – Your Way to Tap into the Tongue-Brain Connection

Our Flexible Y Tool is an innovative microcurrent tongue stimulator that can help “rewire the brain” by accessing the pons. Using a microcurrent device, the tongue can be stimulated, accessing this “gatekeeper of the brain.”
The Flexible Y Tool is made of comfortable plastic and can be easily adjusted to reach the appropriate areas of the tongue. It has been shown to provide relief for balance problems and dizziness, making it an effective tool for accident victims and those taking certain medications. This accessory is available in bulk for physicians who want one per patient. With the Flexible Y Tool, the possibilities for treating pons and other brain-related issues are endless.
Learn more about treating the pons by watching out the short video below:
Stick Out Your Tongue to Protect Your Brain
The tongue and brain work together in previously unknown ways, influencing our food choices, flavor preferences, and language development. As our understanding of this connection grows, we can expect to see new discoveries and insights into the workings of the human body.
Neuroplasticity refers to the brain’s ability to change and reorganize itself, forming new neural connections and optimizing neural pathways to adapt to new conditions. This ability also allows the brain to compensate for damage and injury in different parts of the brain, indicating that the brain can heal itself under the right conditions.
This concept has huge implications for those who suffer from neurological disorders such as traumatic brain injury, chronic pain, depression, and more.





