Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a therapeutic technique designed to stimulate the vagus nerve, which plays a key role in regulating numerous bodily functions. Traditionally, VNS has been used in medical treatments for conditions such as epilepsy and depression, but recent advancements in microcurrent technology have made non-invasive VNS more accessible.
Microcurrent VNS offers a way to stimulate the vagus nerve without surgery, providing therapeutic benefits for those seeking relief from chronic pain, mental health disorders, and other neurological conditions. This blog will explore the vagus nerve’s role in the body, the differences between traditional and microcurrent VNS, and how you can perform microcurrent VNS effectively.
Understanding Vagus Nerve Stimulation
What is the Vagus Nerve?
The vagus nerve is the longest cranial nerve, connecting the brain to multiple major organs, including the heart, lungs, and digestive system. This nerve has both sensory and motor functions, playing a crucial role in the body’s autonomic nervous system, which regulates involuntary functions like heart rate, digestion, and immune responses.
Location and Function
The vagus nerve originates in the brainstem and extends down through the neck, chest, and abdomen. It sends signals to and from the brain and these key organs, controlling functions such as:
- Heart rate: It slows the heart rate when necessary.
- Digestion: It regulates the muscles responsible for moving food through the digestive tract.
- Immune system: It helps control inflammation in the body.
- Stress response: It shifts the body from a “fight or flight” state to a “rest and digest” state.
Given its extensive influence over critical bodily functions, stimulating the vagus nerve can have profound effects on both physical and mental health.
Traditional vs. Microcurrent VNS
Traditional Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Traditional VNS involves surgically implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. This device is typically used for treating epilepsy and depression when other treatments are ineffective. While effective, traditional VNS comes with risks such as infection, device malfunction, and the need for follow-up surgeries to replace or repair the device.
Microcurrent Vagus Nerve Stimulation
In contrast, microcurrent VNS is a non-invasive alternative that uses low-level electrical currents to stimulate the vagus nerve externally, eliminating the need for surgery. Microcurrent devices offer flexibility and ease of use, allowing individuals to perform the treatment safely from home. These devices can help manage pain, reduce inflammation, and support mental health without the complications associated with surgical procedures.
Check out this new protocol designed specifically for people that are EMF sensitive in a quick 10-minute training:
Benefits of Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Microcurrent VNS offers several therapeutic benefits, making it an attractive option for individuals looking to improve their overall well-being without surgery. The potential benefits include:
Mental Health
- Depression and Anxiety: Microcurrent VNS has shown promise in helping alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety by regulating neurotransmitters and improving mood. By stimulating the vagus nerve, it can help promote relaxation and recovery, lowering stress levels and supporting emotional stability.
Neurological Conditions
- Epilepsy: Traditionally, VNS has been used to manage epilepsy by reducing the frequency and intensity of seizures. Microcurrent VNS offers a non-invasive method for achieving similar benefits, particularly for those who do not respond well to medication.
Pain Management and Inflammation Control
- Chronic Pain and Inflammation: Microcurrent VNS reduces inflammation by shifting the brain into an alpha state, where the body is less able to produce inflammatory responses. It has been used effectively to manage conditions like arthritis, fibromyalgia, and migraines, providing relief from pain and swelling.
Potential Advantages of Microcurrent VNS Over Traditional Methods
Microcurrent VNS offers several advantages over traditional, surgically implanted VNS devices:
- Non-invasive: No surgery is required, making the procedure much safer with fewer risks of complications.
- Convenient: Treatments can be performed at home with simple microcurrent devices.
- Cost-effective: Microcurrent VNS is generally more affordable, as there are no surgical or follow-up costs involved.
Microcurrent Vagus Nerve Stimulation Explained
What is Microcurrent VNS?
Microcurrent vagus nerve stimulation uses low-level electrical currents to stimulate the vagus nerve externally, bypassing the need for invasive surgery. The technology behind microcurrent devices allows for precise control over the electrical currents, ensuring safe and effective stimulation.
How Does Microcurrent VNS Differ from Traditional VNS?
While traditional VNS delivers electrical stimulation directly to the nerve via an implanted device, microcurrent VNS delivers stimulation externally. Microcurrent devices target the same pathways as traditional VNS but do so through the skin, making it a non-invasive procedure.
Scientific Principles Behind Microcurrent Stimulation
The use of microcurrent in therapy is based on the principle that low-level electrical currents can stimulate the body’s natural healing processes. By applying microcurrents to the vagus nerve, the therapy promotes a shift from a beta brainwave state (stress, pain) to an alpha state, which promotes healing and reduces inflammation.
Evidence Supporting Efficacy
Research has demonstrated that microcurrent VNS can be effective in reducing chronic pain, improving mental health, and managing conditions like epilepsy and migraines. Ongoing studies continue to explore its potential in broader applications, from treating autoimmune diseases to supporting cardiovascular health.
How to Perform Microcurrent Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Preparing for the Procedure
Before performing microcurrent VNS, it’s important to ensure you have the proper equipment and understand the process. Make sure you follow the device instructions and observe any contraindications, especially if you have underlying medical conditions.
Necessary Equipment and Tools
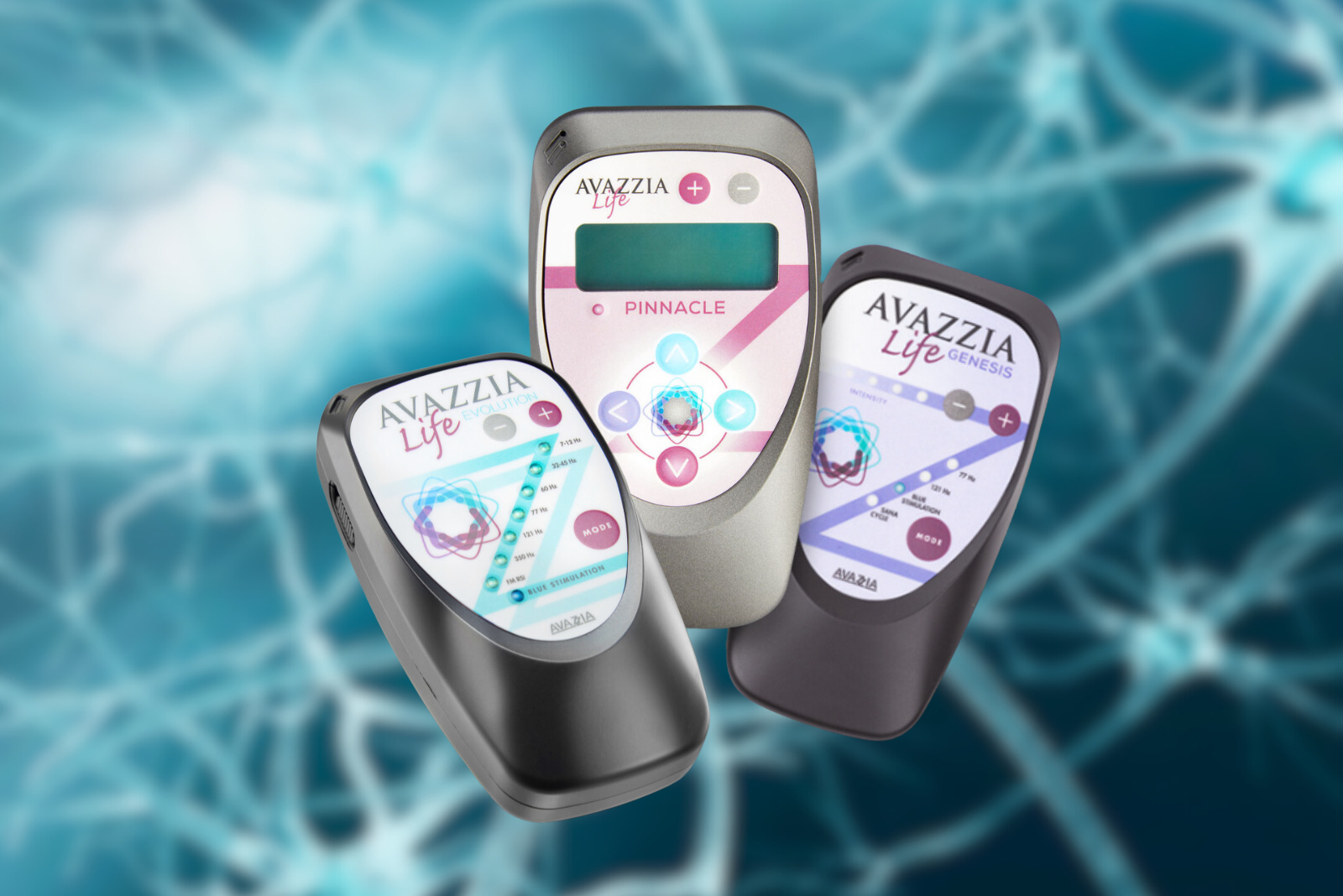
- An Avazzia Life Evolution or Avazzia Life Pinnacle (with 7-12 Hz)
- Y electrode or vagus nerve conductive pad
Step-by-Step Guide
Preparation
- Set up the device according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Ensure proper placement of electrodes: For best results, you’ll be placing the electrode on the left side of the neck.
Execution
- Adjust the settings: Set the device to a low-frequency range of 7-12 Hz.
- Place the electrode on the left side of the neck, slightly behind the carotid artery.
- Monitor the response: You should feel a mild tingling sensation or a slight “jiggling” effect during treatment. Run the program for 3 minutes 3-4 times per day.
Comparing Microcurrent VNS to Other Methods
Traditional VNS
Traditional VNS involves surgery and carries risks of infection, device malfunction, and the need for replacement surgeries. In contrast, microcurrent VNS offers a safer, non-invasive option.
Holistic VNS
From gargling, to meditation, to humming and singing, there are many ways to stimulate the vagus nerve. The downside is that this requires practice, and can be a challenge to initiate whereas microcurrent VNS stimulation can be done by even the most novice user and guarantees that vagal activation.
Surgical vs. Non-Surgical Options
Surgical VNS remains a choice for patients with severe epilepsy or depression, but for those seeking non-invasive treatments, microcurrent VNS is an attractive alternative.
Other Neuromodulation Techniques
Other techniques like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) also provide non-invasive neuromodulation, but VNS specifically targets the vagus nerve, offering more direct effects on the autonomic nervous system.
Future Directions and Research
Emerging Trends in VNS Technology
The future of VNS technology includes more portable, user-friendly devices that are easy to use at home. Researchers are exploring the potential for VNS to treat a wider range of conditions, including inflammatory diseases, cognitive disorders, and even metabolic issues like obesity.
Ongoing Studies and Advancements
Studies are underway to better understand how vagus nerve stimulation affects the body and mind, with researchers looking into its potential for treating conditions like PTSD, autoimmune disorders, and heart disease.
The Power of Microcurrent Vagus Nerve Therapy
 Microcurrent vagus nerve stimulation is a non-invasive, effective therapy for managing pain, reducing inflammation, and improving overall health. By targeting the vagus nerve, this treatment helps regulate vital bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and mental well-being, without the need for surgery. Its benefits extend to conditions like chronic pain, anxiety, depression, and neurological disorders.
Microcurrent vagus nerve stimulation is a non-invasive, effective therapy for managing pain, reducing inflammation, and improving overall health. By targeting the vagus nerve, this treatment helps regulate vital bodily functions, including heart rate, digestion, and mental well-being, without the need for surgery. Its benefits extend to conditions like chronic pain, anxiety, depression, and neurological disorders.
With ongoing advancements in VNS technology, microcurrent stimulation is becoming an accessible and practical solution for many. Whether you are new to this therapy or already using it, microcurrent VNS can be an important part of a holistic approach to health and wellness.
If you’re new to microcurrent therapy and would like to explore it further, contact us at concierge@painfreeforlife.com or text +1 415-688-2045. For current device owners, your treatment coordinator is available to guide you. You can also join our supportive community by visiting the Pain Free for Life Support Group on Facebook.





